반응형
문제 정의하기
- 폴란드의 브로츠와프 의과대학에서 2013년 공개한 폐암 수술 환자의 수술 전 진단 데이터와 수술 후 생존 결과를 기록한 실제 의료 기록 데이터
- 이진 분류 예제에 적합한 데이터셋은 17개 변수(종양의 유현, 폐활량, 호흡곤란 여브, 기침, 흡연, 천식 여부 등의 17가지 환자 상태), 18번째는 수술 후 생존 결과로 1이면 생존, 0이면 사망 폐암환자 수술 예측 데이터 셋
- 17개 변수를 독립변수로 보고 생존 유무를 예측하는 이진 분류 문제로 정의
데이터 준비하기
- https://www.kaggle.com/sojinoh/thoraricsurgery-dataset
데이터셋 생성하기
- 입력(속성값 17개) 출력(판정결과 1개) 변수 90:10 비율 학습 데이터 : 423건, 테스트 데이터:47건 → 총 데이터 470건
모델 구성하기
- Dense 레이어만을 사용하여 다층 퍼셉트론 모델을 구성데이터 준비하기
- 속성이 17개이기 때문에 입력 뉴런을 17개이고, 퍼셉트론 개수 30, 활성화 함수 relu,
두번째 Dense 레이어 뉴런 퍼셉트론 개수 20, 활성화 함수 relu,
세번째 Dense 레이어 뉴런 퍼셉트론 개수 10, 활성화 함수 relu,
마지막 출력 Dense 레이어 이진 분류이기 떄문에 0~1 사이의 값을 나타내는 출력 뉴런이 1개 활성화 함수 sigmoid
모델 학습과정 설정하기
- 모델을 정의했다면 모델을 손실함수와 최적화 알고리즘(하이퍼파라미터) 설정
- loss : 이진 클래스 문제이므로 'binary_crossentropy'으로 지정
- optimizer : 효율적인 경사 하강법 알고리즘 중 하나인 'adam'을 사용
- metrics : 평가 척도를 나타내며 분류 문제에서는 일반적으로 'accuracy'으로 지정
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])모델 학습시키기
- epochs=100, batch_size=64
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=100, batch_size=64)모델 평가하기
scroes = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test)
print('%s : %.2f%%' %(model.metrics_names[1], scores[1]*100))실습하기
데이터 준비하기
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import tensorflow as tf
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
# 랜덤 시드 고정
np.random.seed(5)dataset = pd.read_csv('/content/ThoraricSurgery.csv', header=None)
dataset
데이터셋 분리하기 - 입력(feature 17), 출력(label, 1) 분리
X = dataset.iloc[:, :-1]
y = dataset.iloc[:, -1]
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.1, random_state=777)X_train.shape
모델 구성하기
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(30, input_dim=17, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(20, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(10, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))model.summary()
모델 설정하기
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])모델 학습하기
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=100, batch_size=64)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
his_dict = history.history
loss = his_dict['loss']
epochs = range(1, len(loss) + 1)
fig = plt.figure(figsize = (10, 5))
# 훈련 및 검증 손실 그리기
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1)
ax1.plot(epochs, loss, color = 'orange', label = 'train_loss')
ax1.set_title('train loss')
ax1.set_xlabel('epochs')
ax1.set_ylabel('loss')
ax1.legend()
acc = his_dict['accuracy']
# 훈련 및 검증 정확도 그리기
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2)
ax2.plot(epochs, acc, color = 'blue', label = 'train_accuracy')
ax2.set_title('train accuracy')
ax2.set_xlabel('epochs')
ax2.set_ylabel('accuracy')
ax2.legend()
plt.show()
모델 평가하기
scores = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test)
print('%s : %.2f%%' %(model.metrics_names[1], scores[1]*100))
scores = model.evaluate(X_train, y_train)
print('%s: %.2f%%' %(model.metrics_names[1], scores[1]*100))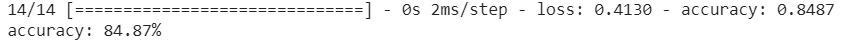
LIST